
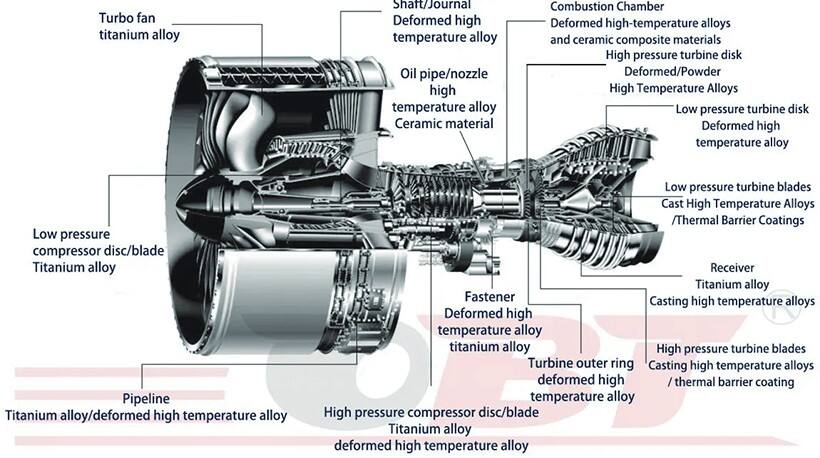
Turbine wheels, also known as turbine impellers or turbine rotors, are critical components invarious mechanical systems, including turbochargers, gas turbines, steam turbines, and waterturbines. These wheels are designed to convert the kinetic energy of a fluid (such as air, gas,steam, or water) into rotational mechanical energy.
Video
Features
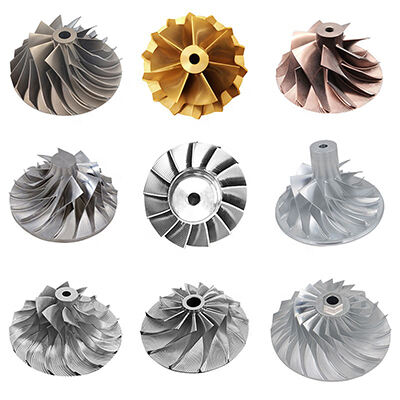

Turbine impellers have intricately designed blades orvanes shaped to efficiently capture the kinetic energyof a fluid (such as air, gas, steam or water) and convertit into rotating mechanical energy. The shape, angleand arrangement of the blades are optimized formaximum energy transfer and minimum aerodynamiclosses.
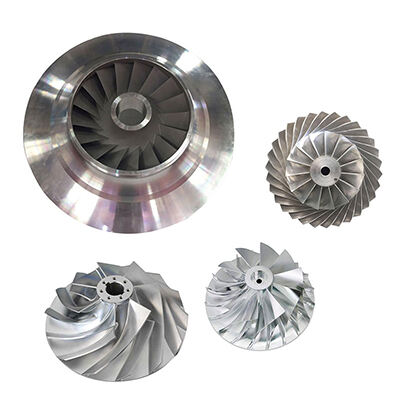

Turbine impellers are typically made of high-strength,heat-resistant materials such as nickel-based superalloysor titanium alloys. These materials were chosen for theirability to withstand the high temperatures, mechanicalstresses and corrosive environments encountered duringoperation.

Turbine wheels must be precisely balanced to ensuresmooth operation, minimize vibration, and preventpremature wear or damage to bearings and othercomponents. Imbalance can lead to excessive noise,reduced efficiency and potential mechanical failure.
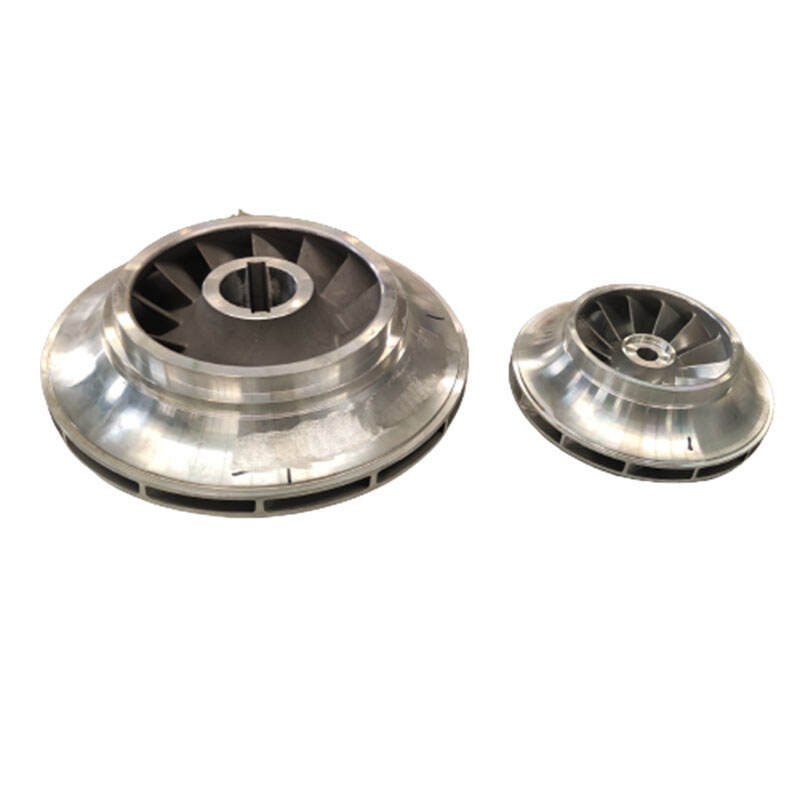

In high temperature applications, the turbine wheel mayhave an internal or external cooling system to dissipate heatand maintain thermal stability. Cooling channels or channelswithin the wheel may allow coolant fluid or air to circulate to extract excess heat generated during operation.
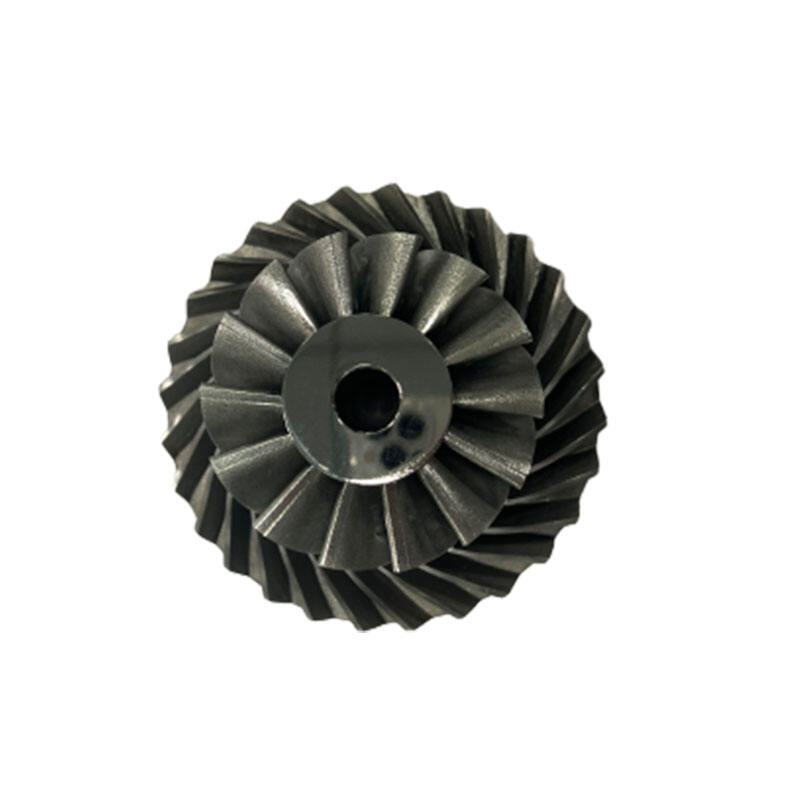

The turbine wheel is subjected to huge centrifugal forcesand mechanical loads during rotation. Proper considerationof rotor dynamics, including rotor stiffness, naturalfrequencies and critical speeds, is critical to preventingresonance, chatter and other dynamic instabilities that canharm performance and reliability.
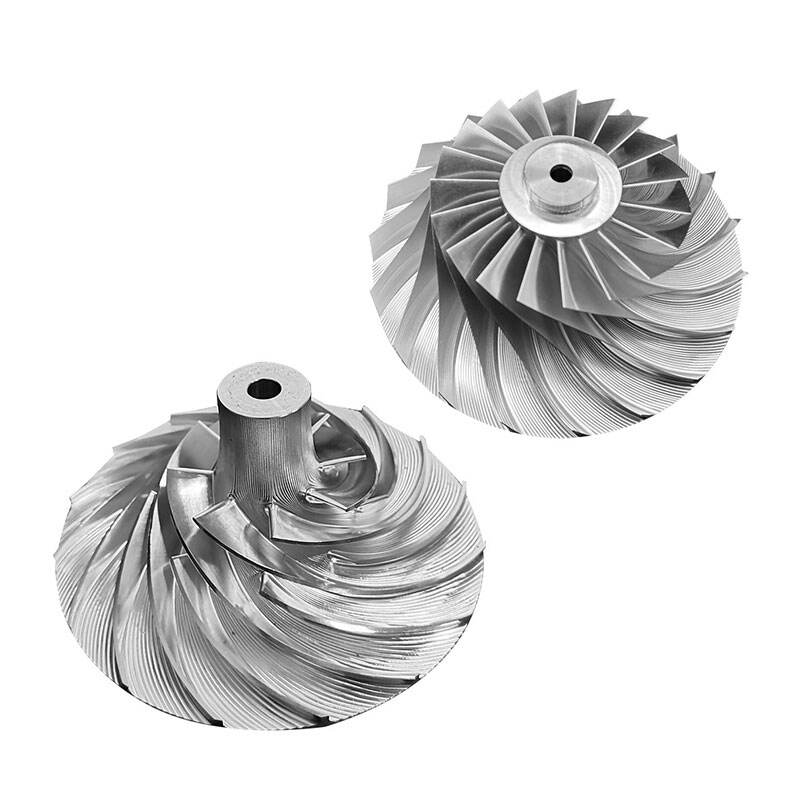

Turbine impellers are typically manufactured usingadvanced machining and casting techniques to achievetight tolerances, smooth surfaces and precise geometry.High-precision manufacturing processes ensure consistentblade profiles, consistent material properties and reliableperformance from production batch to batch.
material
Inconel material Hastelloy material Stellite material Titanium material Nimonic Alloy material
A turbine disk, also known as a turbine rotor disk, is a crucial component in gas turbines, steam turbines, and other types of turbines. It plays a central role in converting fluid energy (such as gas or steam) into mechanical energy.
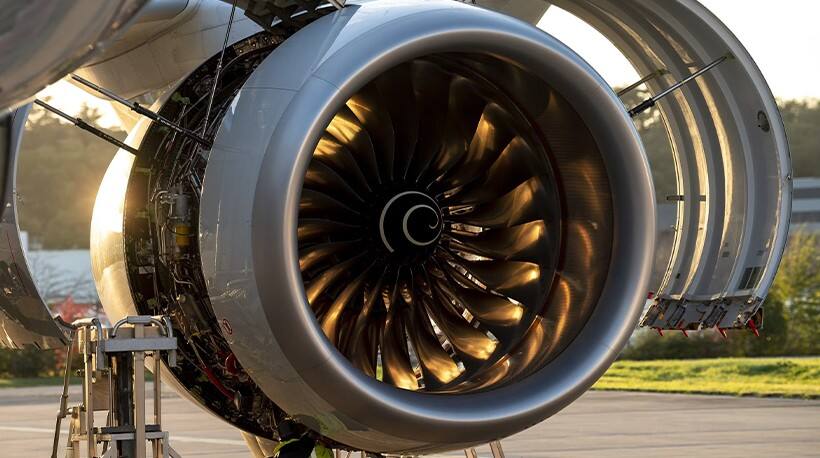

Aerospace field:Turbine discs are widely used in aerospace engines, including jet engines,turbofan engines, etc. They carry the turbine blades, which rotate to drive thecompressor, turbine and other related components to provide power tosupport the flight of the aircraft.

Energy industry:In the energy field, turbine disks are used in steam turbines, gas turbines,steam turbines and other equipment in various types of generating units.They convert gas or steam energy into electrical energy for use in powergeneration plants by turning the rotor of a generator.

Industrial field:In the industrial field, turbine disks are used in various types ofturbomachinery equipment, such as compressors, fans, pumps, etc. Theyrealize the compression, transportation or circulation of fluids or gasesthrough rotation and are used for power transmission and energy conversionin industrial production, manufacturing and processing processes.
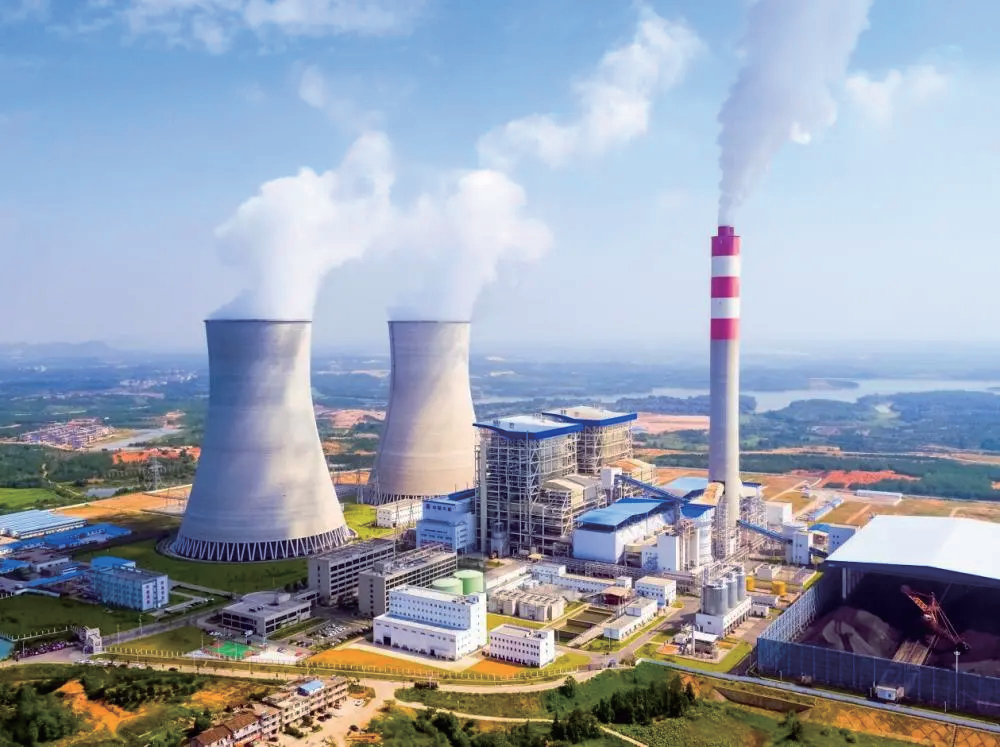

Industrial field:In the energy extraction field, turbine disks are used in various turbinemachinery equipment, such as oil and gas extraction equipment,hydroelectric power generation equipment, etc. They drive relatedequipment through rotation to improve energy extraction efficiency andproductivity
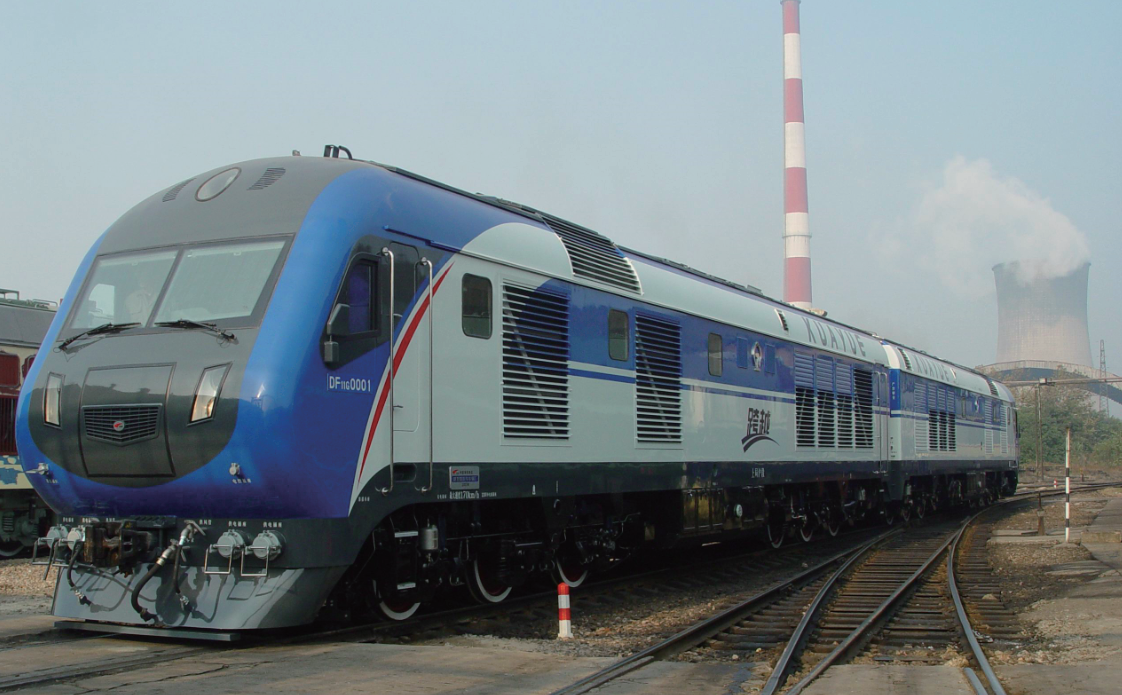

Transportation field:Turbine blades are used in turbochargers in automobile engines to improveengine power and fuel efficiency, as well as in turbochargers for transportationvehicles such as trains and ships.
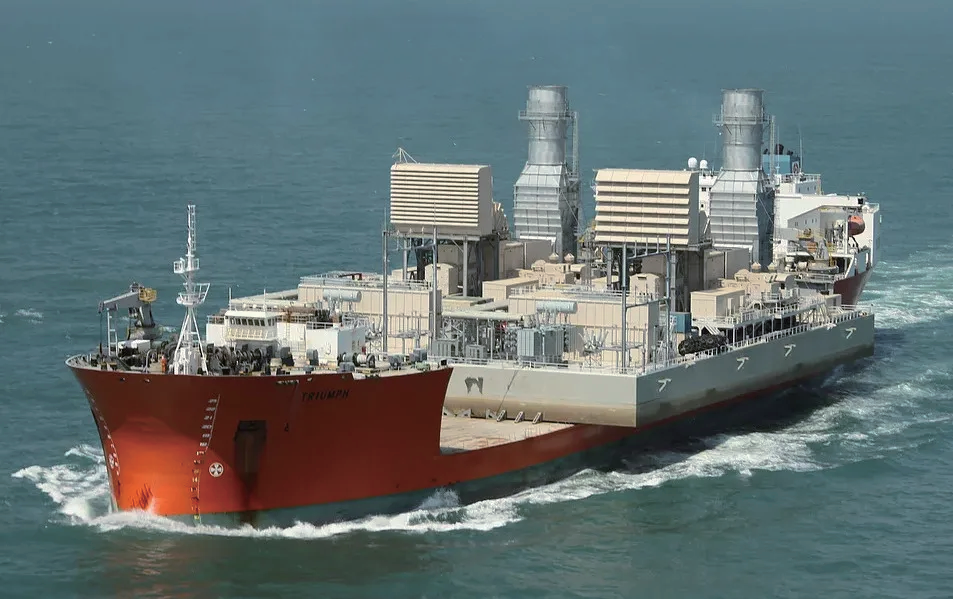

Shipbuilding industry:Turbine blades are used in ship power devices, such as turbochargersand marine turbines, to provide power to drive ships.
Our professional sales team are waiting for your consultation.