
Stellite cobalt-based alloys consist of complex carbides in the alloy matrix. They are resistant to abrasion, abrasion and corrosion and retain these properties at high temperatures. Its excellent wear resistance is mainly attributed to the unique inherent properties of the hard carbide phase dispersed in the CoCr alloy matrix.
Stellite 21 (formerly Stellite 8) developed
It emerged in the mid-1930s as a corrosion-resistant CoCr alloy and quickly found application as a biocompatible hip implant and denture alloy. Many alloys currently used in medical applications are variations of the original Stellite 21 composition. It was also one of the first heat-resistant alloys attempted for use in jet engines.
Stellite 21 consists of a CoCrMo alloy matrix containing dispersed hard carbides, which strengthen the alloy and increase its hardness, but also reduce ductility. The type, shape, size and distribution of carbides are strongly affected
Due to the processing history of the alloy, the mechanical properties of Stellite 21 are highly dependent on the manufacturing route and any subsequent heat treatment.
Due to the low carbide volume fraction, the cobalt-based alloy matrix dominates the wear and corrosion properties. Stellite 21 has excellent resistance to cavitation, abrasion and metal-to-metal sliding wear but is not recommended for severe hard particle wear. During wear and even during machining, the surface hardens significantly and using the correct machining tools and techniques is important to obtain the best results.
Stellite 21 offers excellent resistance to thermal and mechanical shock. Optimum high temperature strength is achieved by solution heat treatment at 1200–1240C (2190–2265F), followed by quenching and aging in the temperature range 700–1150C (1290–2100F).
Stellite 21 can be cast, powder metallurgically processed or used as a welding hard facing. Recommended for applications involving cavitation, erosion, corrosion and/or high temperatures, such as petrochemical and power generation valve trim. Due to its good impact resistance, it is widely used in the manufacture of forging or hot stamping dies. Oxyacetylene welding deposition methods are not recommended for this alloy.
product
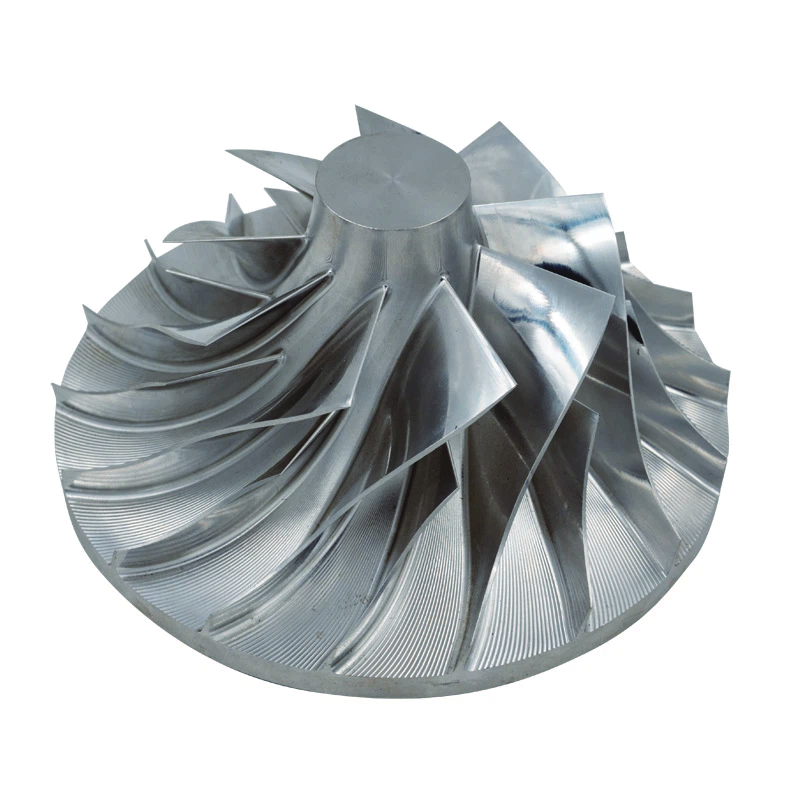

turbine wheel
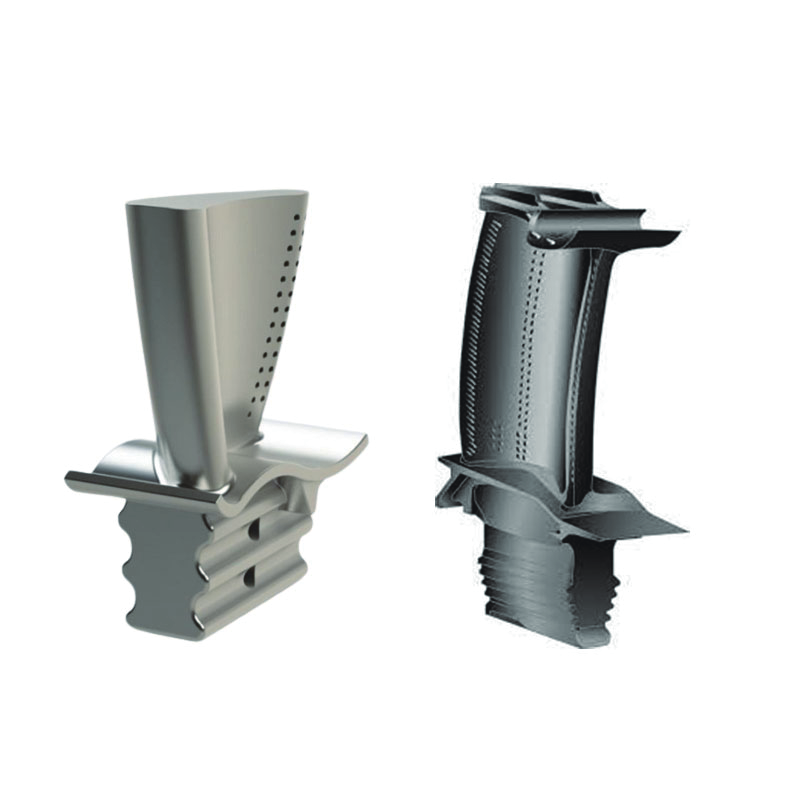

turbine blade
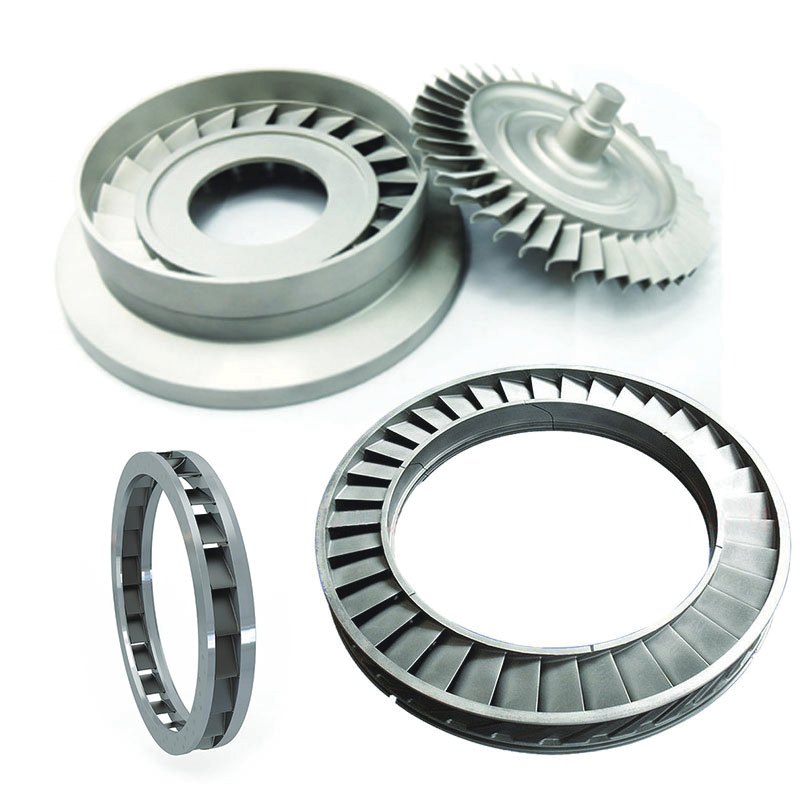

nozzle ring
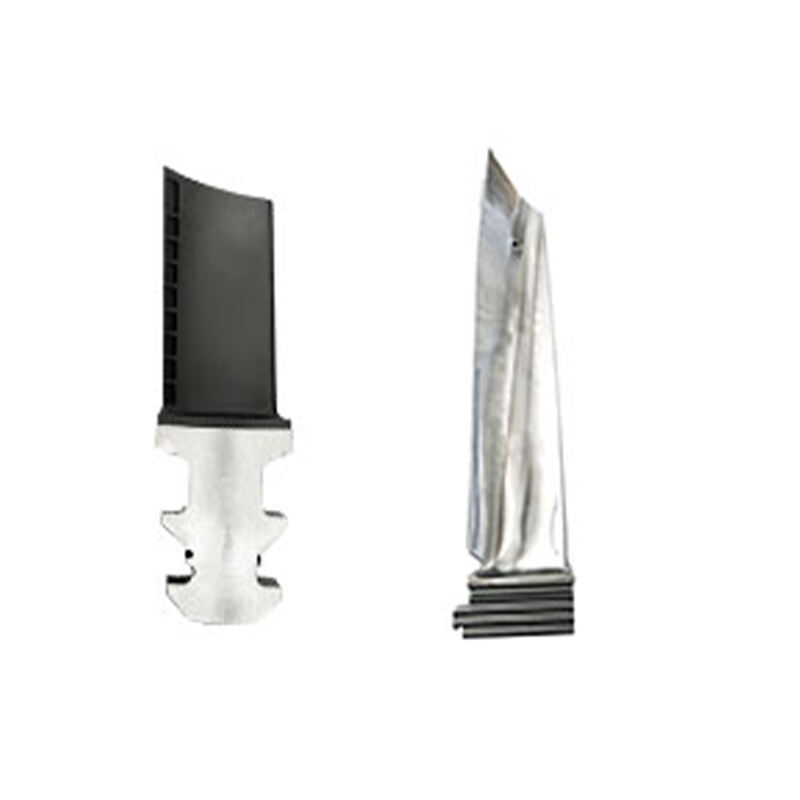

compressor blade
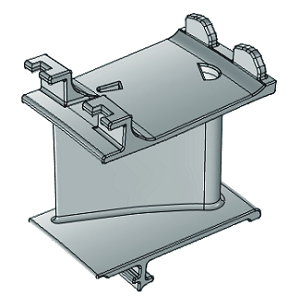
guide vanes
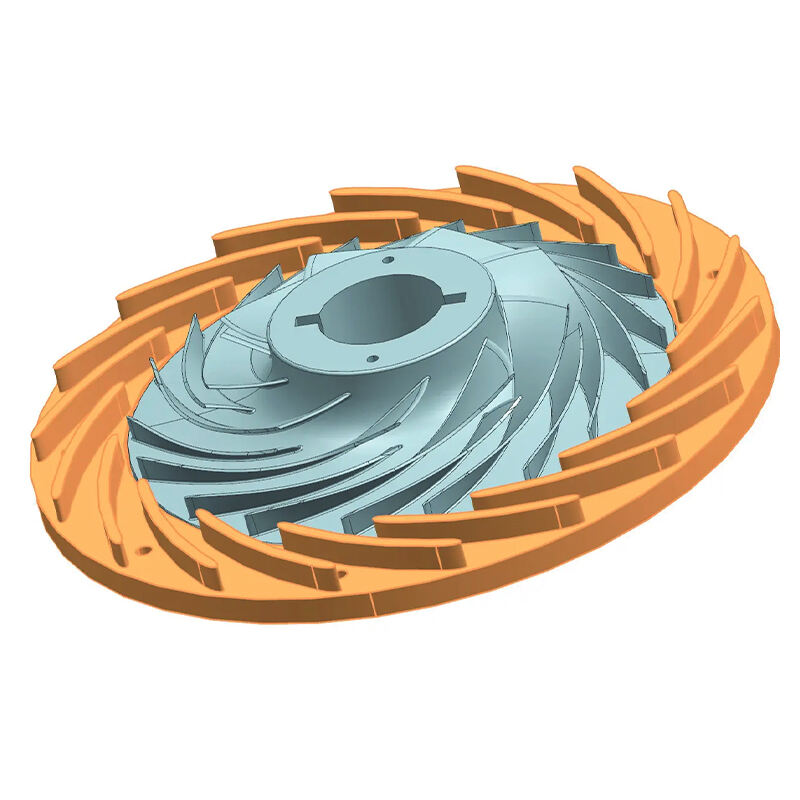
diffuser
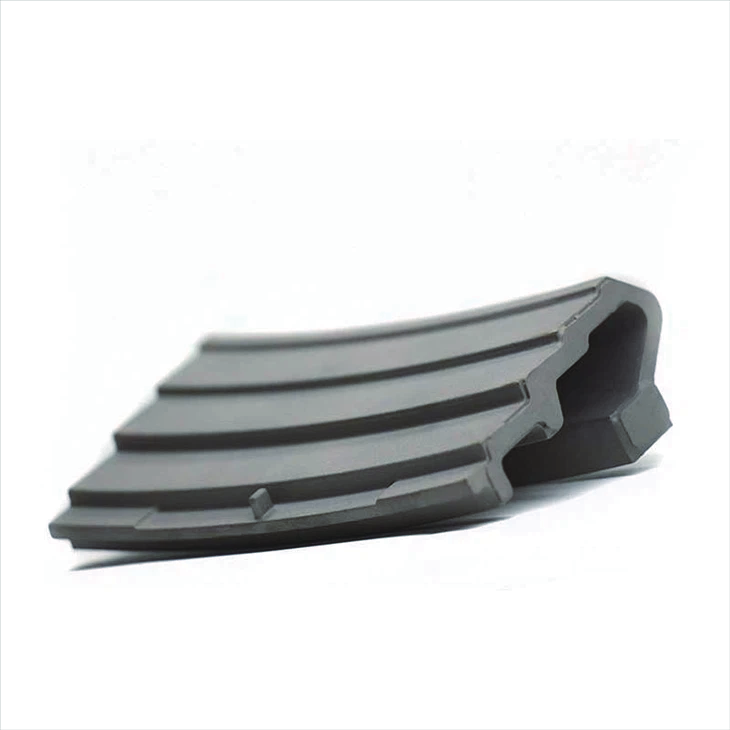

Segment
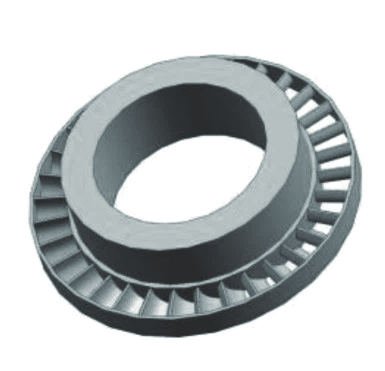
Turbine Rotor
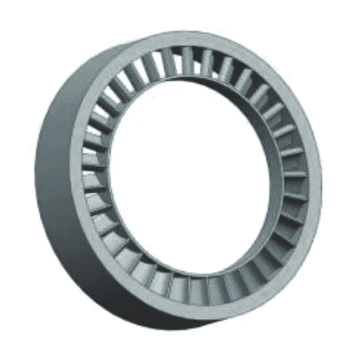
Turbine Stator

Stellite sheet

Stellite pipe

Stellite rod
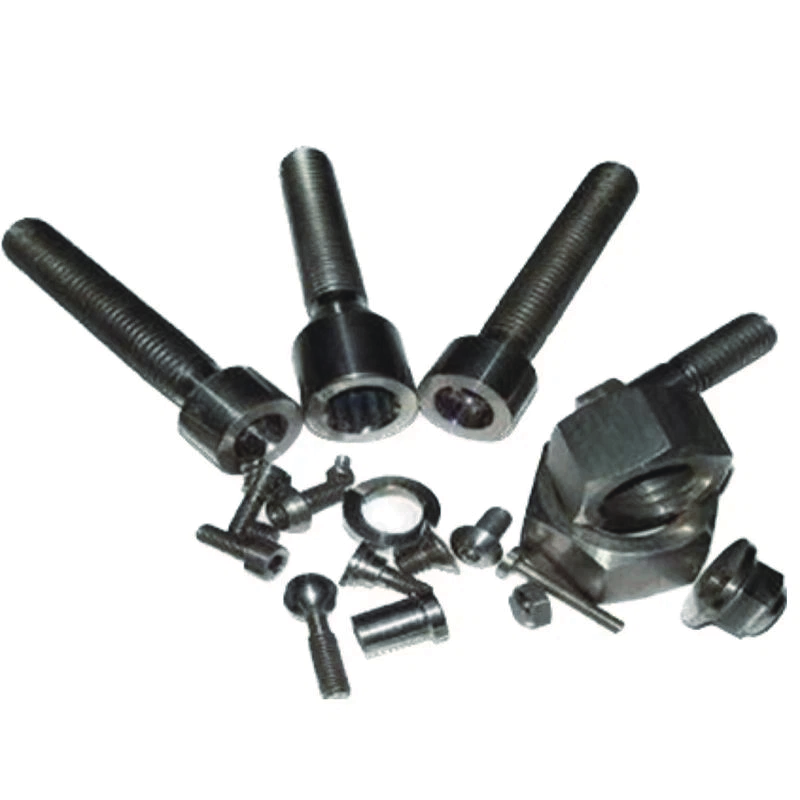

Stellite bolt and nut

Stellite Fasteners

Stellite wire

spring
According to drawings or samples
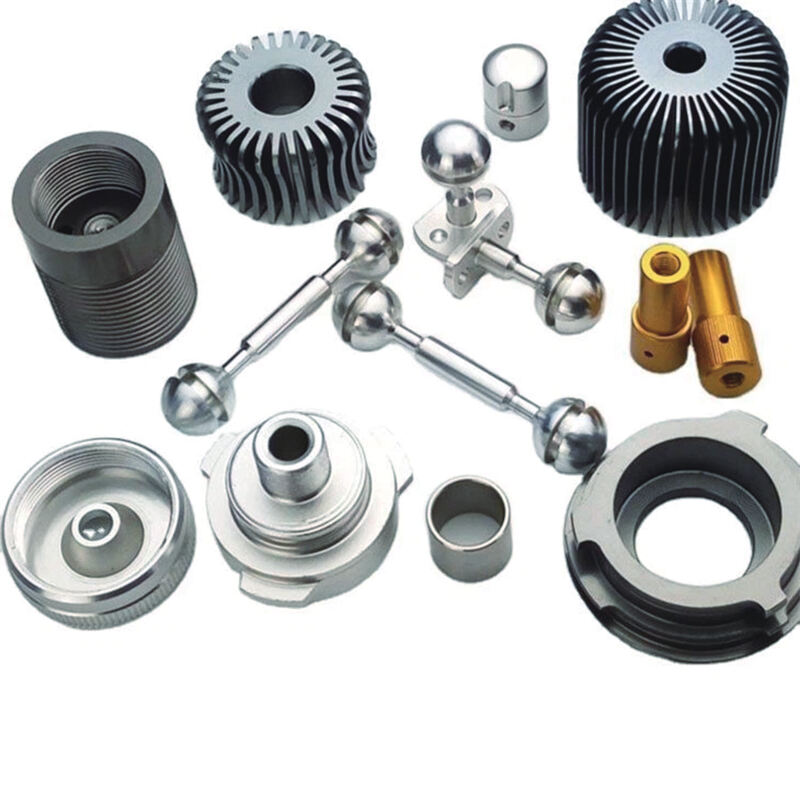
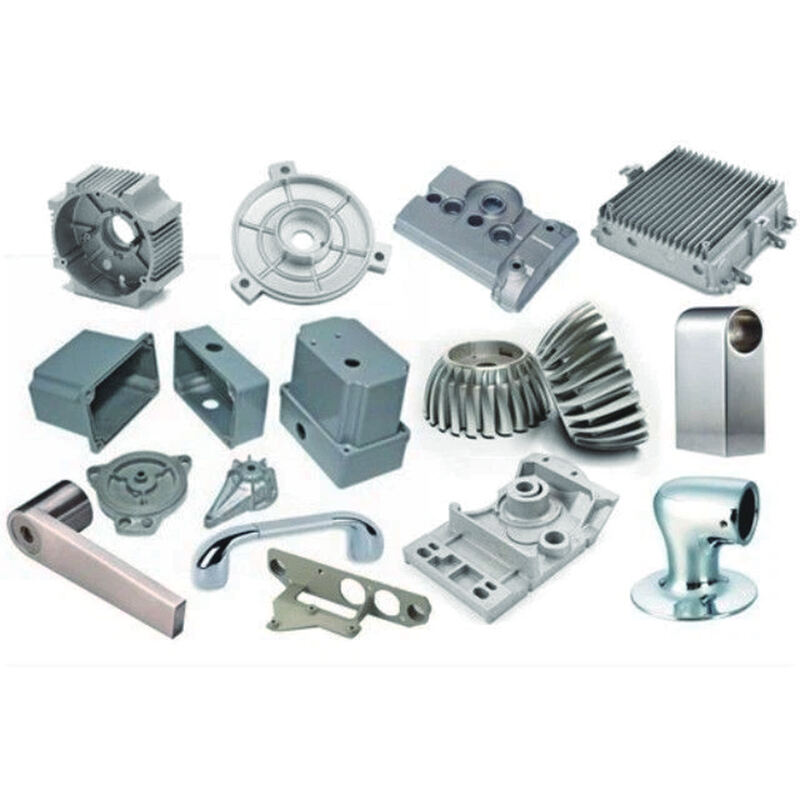
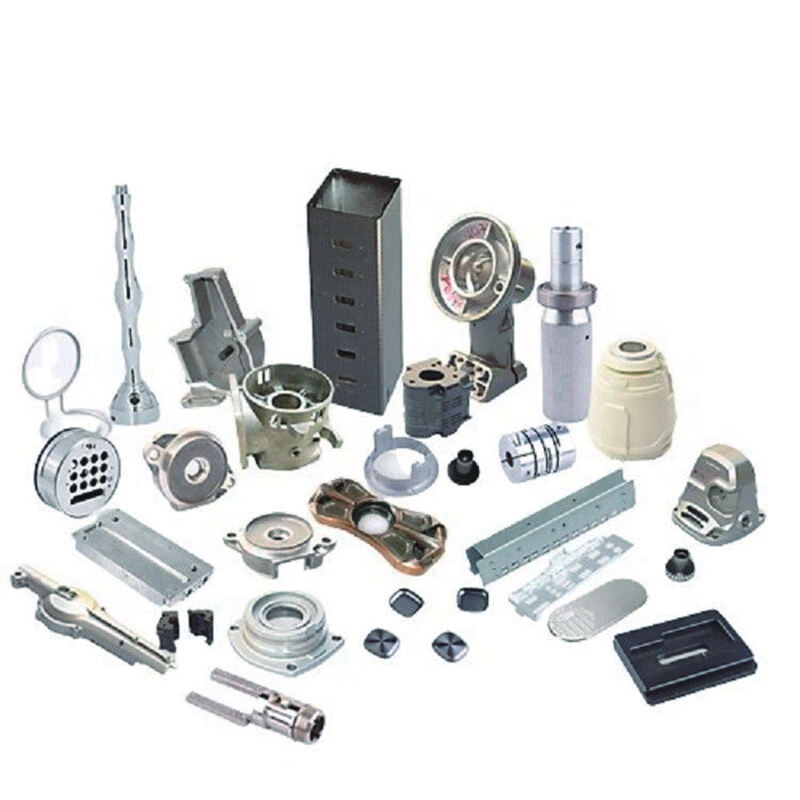
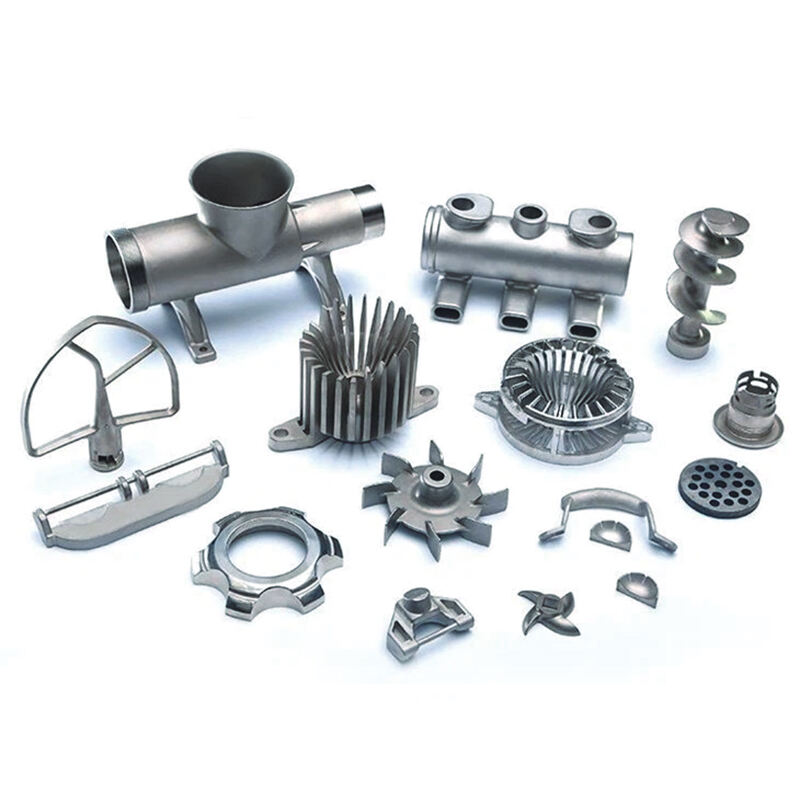




Nominal Composition (Mass %) and Physical Properties
| Co | Cr | Mo | C | Ni | Others | Hardness** | Density | Melting Range |
| Base | 26-29 | 4.5-6.0 | <0.35 | <3.0 | Fe, Si, Mn | 27-40 HRC**290-430 HV** | 8.33 g/cm30.301 lb/in3 | 1295-1435ºC2360-2615ºF |
Stellite alloys are a group of cobalt-chromium alloys known for their exceptional wear resistance, high temperature performance and corrosion resistance. Here's an overview of Stellite:
Composition:
Stellite alloys are primarily composed of cobalt (about 50-65%) and chromium (about 25-30%), with varying proportions of tungsten, carbon and other elements depending on the grade. These alloying elements give Stellite alloys a unique combination of properties.
Wear Resistance:
Stellite alloys are known for their excellent wear resistance, making them suitable for applications where components are subject to abrasive wear, erosion and sliding contact. They are typically used in high-wear environments such as cutting tools, saw teeth, valve seats, and pump components.
High Temperature Performance:
Stellite retains its mechanical properties at high temperatures, allowing it to withstand high temperatures without significant loss of strength or hardness. This makes Stellite alloys suitable for high-temperature applications such as gas turbine components, furnace components and exhaust valves.
Corrosion Resistance:
Stellite alloys exhibit good corrosion resistance in a variety of environments, including acidic and alkaline solutions, as well as high-temperature gases and molten salts. This corrosion resistance makes Stellite alloys suitable for use in chemical processing, marine engineering, and oil and gas production.
Versatility:
Stellite alloys are available in a variety of grades and forms, including powders for thermal spray coatings, castings and forgings such as rods and plates. This versatility allows the selection of the most appropriate grade and form of Stellite alloy for a specific application.
Applications:
Stellite alloys are widely used in aerospace, automotive, oil and gas, power generation and manufacturing industries. They are widely used in components requiring wear resistance, high temperature performance and corrosion resistance.

Aerospace field

Automobile and motorcycle manufacturing

Chemical industry

Marine engineering
Our professional sales team are waiting for your consultation.