Gas turbines are mainly composed of three major components: compressor, combustion chamber and gas turbine. The gas turbine cycle is generally called a simple cycle. Most gas turbines use a simple cycle scheme, and only heavy-duty gas turbines use a combined cycle scheme. Due to different historical backgrounds, gas turbines have developed in different technical paths. Industrial and marine aero-derivative light gas turbines (commonly known as "aero-derivative machines") are formed by modifying aircraft engines; industrial heavy-duty gas turbines (commonly known as "industrial machines") are developed following the traditional steam turbine concept, which are mainly used for mechanical drives and large power stations.
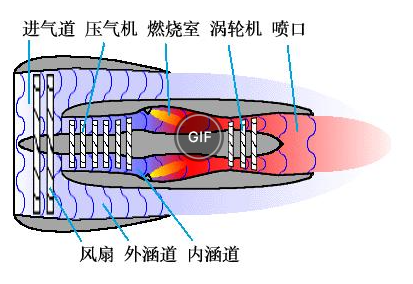
A gas turbine can be divided into three parts from left to right: compressor (blue), combustion chamber (red), and turbine (yellow).
There are dozens of companies engaged in gas turbine research, design, and manufacturing in the world. Currently, the four companies that have fully mastered heavy-duty gas turbine technology are General Electric of the United States, Siemens of Germany, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries of Japan (which introduced Westinghouse technology from the United States in the early days), and Ansaldo of Italy. According to Mr. Chen Xuewen, Vice Chairman of Shanghai Electric Gas Turbine Co., Ltd., there has never been an international standard for the model level of gas turbines, and it is becoming increasingly vague today. The author can only collect opinions from various parties and summarize them as follows:
1. according to the combustion temperature of the gas turbine is divided (every 100 degrees is a level) :
United States GE (Harbin electric introduction) : 1100℃ for E class, 1200℃ for F class, 1400℃ for H class.
Japan Mitsubishi (introduced by Dongfang Electric) : 1400℃ is F class, 1500℃ is G class, H class is intermediate test product, 1600/1700℃ is J class.
Germany Siemens (Shanghai Electric introduction) : the old number V64.3A, V84.3A, V94.3A is 6F class. In 1997, Westinghouse sold its non-nuclear generator division to Siemens. The new number was changed to similar SGT6-5000F and SGT-8000H. Class F is 1200 ° C and Class H is 1500 ° C.
2. Classification of reference output for heavy-duty gas turbines:
Heavy-duty gas turbines for power generation are usually classified according to output when the combustion chamber combustion temperature is between 1100 degrees Celsius and 1500 degrees Celsius. For example, the output of Class B gas turbines is less than or equal to 100MW, the output of Class E gas turbines is between 100MW and 200MW, the output of Class F gas turbines is between 200MW and 300MW, and higher grades such as Class G and Class H are in the range of 300MW to 400MW. According to Mr. Chen Xuewen, because the output of gas turbines of various manufacturers has developed rapidly, this classification method is slightly behind the actual product.
Siemens: The representative product SGT5-8000H super gas turbine weighs 390 tons (equivalent to a fully fueled Airbus A380), is 13.1 meters long, 4.9 meters wide, 4.9 meters high, and has a combined cycle power of 595MW. The power generation of one SGT5-8000H is enough to power a large industrial city. Its turbine blades have to withstand a high temperature of more than 1500°C, which exceeds the turbine inlet temperature of the GE90 turbofan aircraft engine and the F404 jet engine. Since the tip speed of the turbine blade exceeds 1700 kilometers per hour, the huge centrifugal force makes one end of each blade contact 10,000 times the gravity of the earth. The blade cannot have any flaws, and the error is only tens of microns, otherwise it will be scrapped. Therefore, it is said that a blade is equivalent to a BMW.
Mitsubishi Corporation: The latest model is the M701J super gas turbine with a combined cycle power of 650MW. It is equipped with a 15-stage axial compressor with a pressure ratio of 23:1. The burner and the 4-stage axial turbine are all air-cooled, and the first 3 stages use the latest high-temperature protective coatings, ceramic thermal barrier coatings and high-performance air film cooling and other high-tech technologies. With the world's highest gas turbine inlet temperature of 1600°C, it can still ensure the long-term life of high-temperature components. The latest innovations in the J series are designed to further reduce carbon emissions. In March 2020, MHPS received an order for two M501JAC powertrains from the Intermountain Power Authority in Utah, USA. The two gas turbines are based on an air-cooled dry low-NOx combustion system and are capable of using up to 30% renewable hydrogen fuel. Compared with coal-fired power plants of the same size, a 30% hydrogen system will reduce carbon emissions by more than 75%, while a 100% hydrogen system will completely eliminate carbon emissions. Between 2025 and 2045, the plant will gradually achieve 100% renewable hydrogen electricity generation.

General Electric: 9HA series heavy-duty gas turbines are the most efficient combined cycle gas turbines in the world; its latest 9HA.02 heavy-duty gas turbine not only has a combined cycle efficiency of more than 64%, but also has a power output of up to 826MW. These two key indicators far exceed its two major competitors, and the most cutting-edge 3D printing technology is used to manufacture key components.

Thank you for your interest in our company! As a professional gas turbine parts manufacturing company, we will continue to be committed to technological innovation and service improvement, to provide more high-quality solutions for customers around the world.If you have any questions, suggestions or cooperation intentions, we are more than happy to help you. Please contact us in the following ways:
WhatsAPP:+86 135 4409 5201
E-mail:[email protected]
 Hot News
Hot News2024-12-31
2024-12-04
2024-12-03
2024-12-05
2024-11-27
2024-11-26
Our professional sales team are waiting for your consultation.