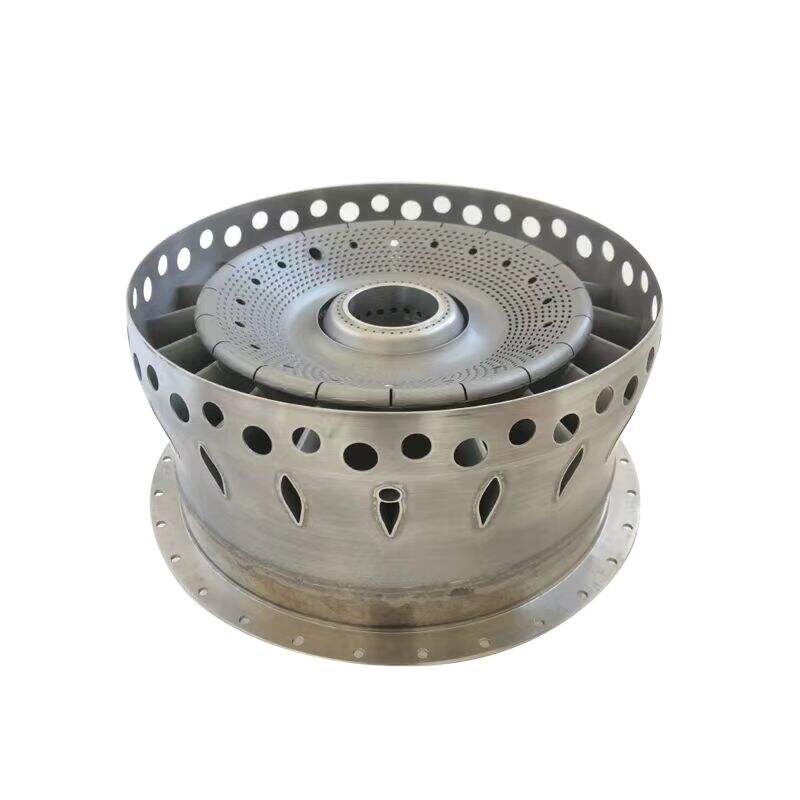

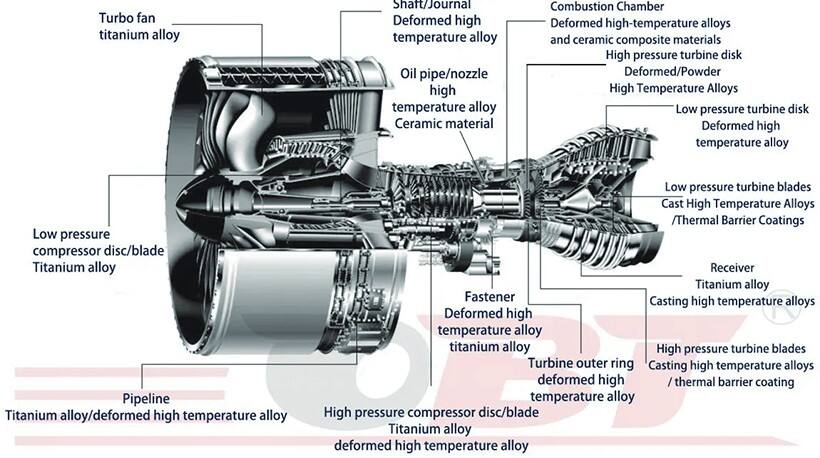
The combustor, also known as the combustion chamber, is a crucial component of a gas turbine engine where fuelis mixed with compressed air and ignited to produce high-temperature, high-pressure gases. These gases then expandthrough the turbine section of the engine, driving the turbine blades and ultimately producing thrust.
Video
Here's an overview of the combustor in a gas turbine engine:
Function:
The primary function of the combustor is to efficiently burn fuel to generate hot, high-pressuregases. These gases provide the energy needed to drive the turbine section of the engine, whichin turn powers the compressor and other accessories.
Fuel Injection:
Fuel is injected into the combustor along with compressed air from the engine's compressor.The fuel-air mixture is carefully controlled to achieve the desired fuel-to-air ratio for efficientcombustion. Different types of fuel injection systems, such as atomizers or fuel nozzles, may beused depending on the specific engine design.
Mixing and Combustion:
Once injected, the fuel mixes with the compressed air in the combustor. Ignition sources, suchas spark plugs or igniters, are used to initiate combustion. The fuel-air mixture burns rapidly,releasing heat energy and raising the temperature and pressure of the gases.
Stabilization:
Combustors are designed to stabilize the combustion process and maintain a stable flame front.This is achieved through various design features, such as swirlers, flame holders, andrecirculation zones, which help to evenly distribute the fuel-air mixture and promote efficientcombustion. Cooling:Due to the extremely high temperatures generated during combustion, combustor liners andother components are typically actively cooled to prevent overheating and maintain structuralintegrity. Cooling air may be extracted from the engine's compressor and directed to thecombustor walls through internal passages or film cooling holes.
Emissions Control:
Modern gas turbine engines are designed to minimize emissions of pollutants such as nitrogenoxides (NOx) and particulate matter. Combustor designs may incorporate features such aslean-burn combustion, staged combustion, and advanced fuel injection systems to reduceemissions while maintaining high efficiency. Materials and Construction:Combustor components are typically made from high-temperature alloys or ceramic materialscapable of withstanding the harsh operating conditions within the engine. These materials mustexhibit excellent heat resistance, mechanical strength, and durability to ensure reliablelong-term operation.
Inspection:
Combustors undergo regular inspection and maintenance to detect any signs of wear, erosion,or damage. Non-destructive testing methods, such as borescope inspections and thermalimaging, are used to assess the condition of the combustor components without disassembly
material
Inconel material Hastelloy material Stellite material Titanium material Nimonic Alloy material
The combustor, or combustion chamber, is a critical component in turbine engines, where it plays a vital role in the energy conversion process. It is the section of the engine where fuel is mixed with air and ignited to produce high-temperature, high-pressure gases that drive the turbine. Combustors are used in a variety of applications, including aircraft engines, power generation turbines, and industrial gas turbines
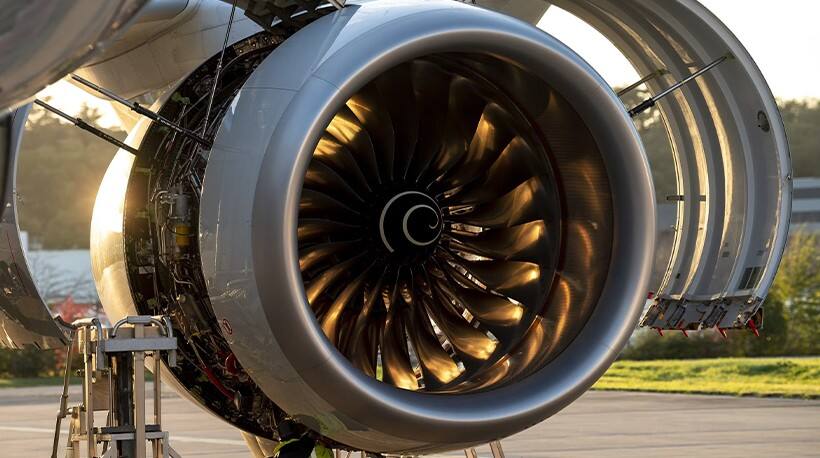

Aerospace field:Turbine combustor are widely used in aerospace engines, including jet engines,turbofan engines, etc. They carry the turbine blades, which rotate to drive thecompressor, turbine and other related components to provide power tosupport the flight of the aircraft.

Energy industry:In the energy field, turbine combustor are used in steam turbines, gas turbines,steam turbines and other equipment in various types of generating units.They convert gas or steam energy into electrical energy for use in powergeneration plants by turning the rotor of a generator.

Industrial field:In the industrial field, turbine combustor are used in various types ofturbomachinery equipment, such as compressors, fans, pumps, etc. Theyrealize the compression, transportation or circulation of fluids or gasesthrough rotation and are used for power transmission and energy conversionin industrial production, manufacturing and processing processes.

Industrial field:In the energy extraction field, turbine combustor are used in various turbinemachinery equipment, such as oil and gas extraction equipment,hydroelectric power generation equipment, etc. They drive relatedequipment through rotation to improve energy extraction efficiency andproductivity

Transportation field:Turbine combustor are used in turbochargers in automobile engines to improveengine power and fuel efficiency, as well as in turbochargers for transportationvehicles such as trains and ships.

Shipbuilding industry:Turbine combustor are used in ship power devices, such as turbochargersand marine turbines, to provide power to drive ships.
Our professional sales team are waiting for your consultation.