
Video
The working principle of high-temperature alloy turbine blades involves aerodynamicprinciples and thermodynamic principles.
Aerodynamic principle: The aerodynamic principle of turbine blades is based on theprinciple of fluid dynamics. When high-temperature and high-pressure gas passes throughthe turbine blades, the airflow will generate a pressure difference on the blade surface, causingthe pressure on both sides of the blade to be different. This pressure difference causes theblades to generate thrust, which drives the turbine disk to rotate. The shape and aerodynamicdesign of turbine blades will affect the flow and pressure distribution of airflow on the bladesurface, thereby affecting the thrust and rotation efficiency of the blades.
Thermodynamic principles: Turbine blades work in high-temperature and high-pressureairflow, so they need to have good heat resistance and corrosion resistance. High-temperaturealloy materials are widely used in turbine blade manufacturing because of their excellenthigh-temperature strength and oxidation resistance. The cooling system of turbine blades alsoplays an important role by introducing cooling media, such as cooling air or liquid, into theinterior or surface of the blades to reduce the surface temperature of the blades and maintainthe stability of the blade structure and material performance.
In summary, high-temperature alloy turbine blades convert gas kinetic energy into mechanicalenergy by utilizing the pressure difference generated by aerodynamic principles, and ensure thestability and durability of the blades in high-temperature and high-pressure workingenvironments through thermodynamic principles. Its design and manufacturing need to fullyconsider aerodynamic performance, material selection, cooling technology and other factorsto ensure that the blades can effectively drive the turbine and operate stably for a long time.
features

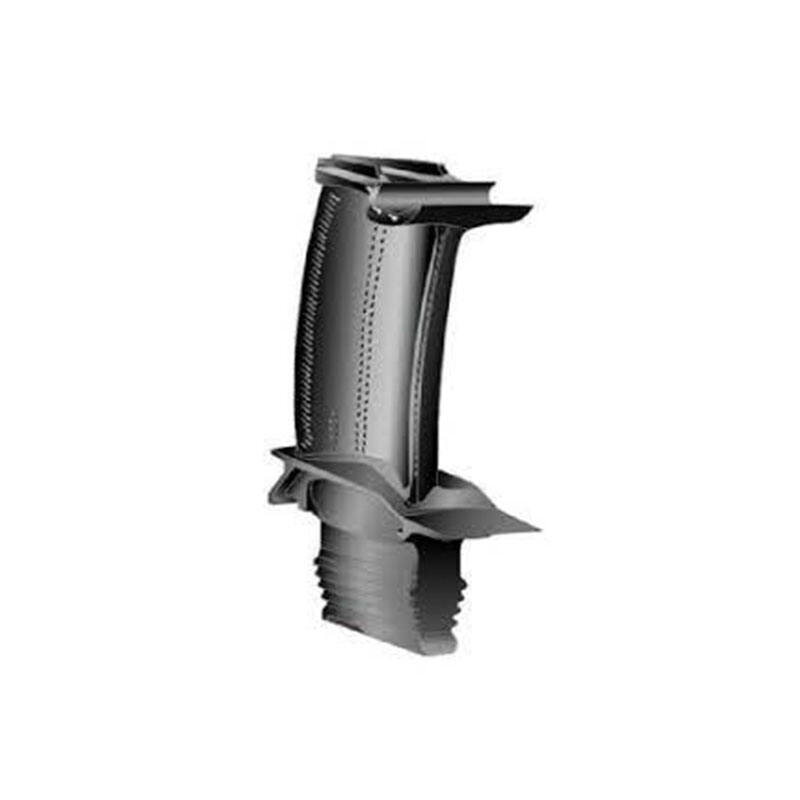
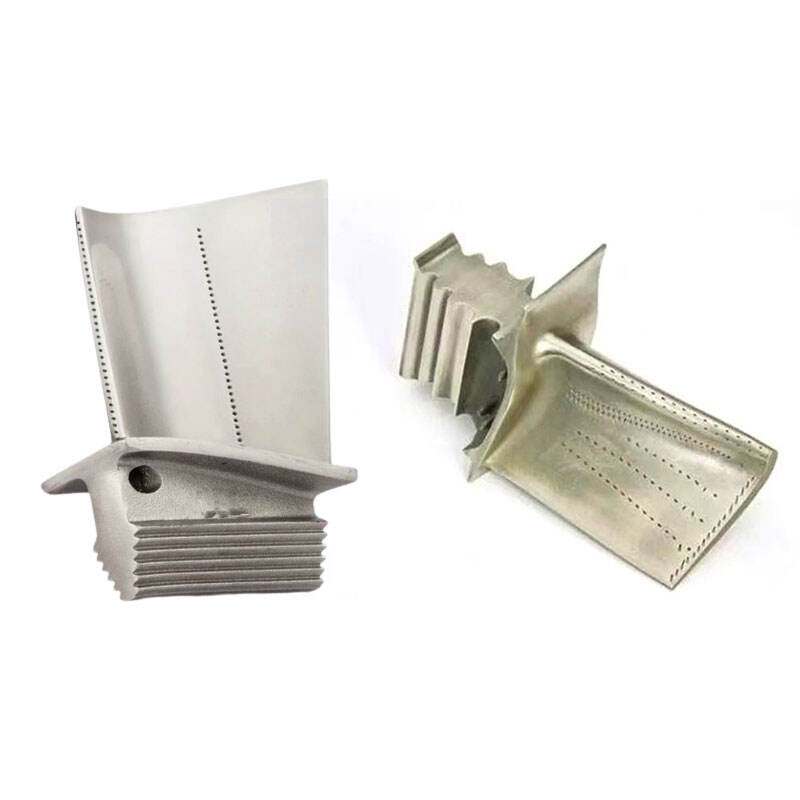
The turbine blade is the main support structurefor fixed blades. The blades are fixed on thedisk to form a rotating blade array. Theseblades generate power through the impact ofairflow, thereby pushing the turbine disk torotate and driving related mechanicalequipment to operate.

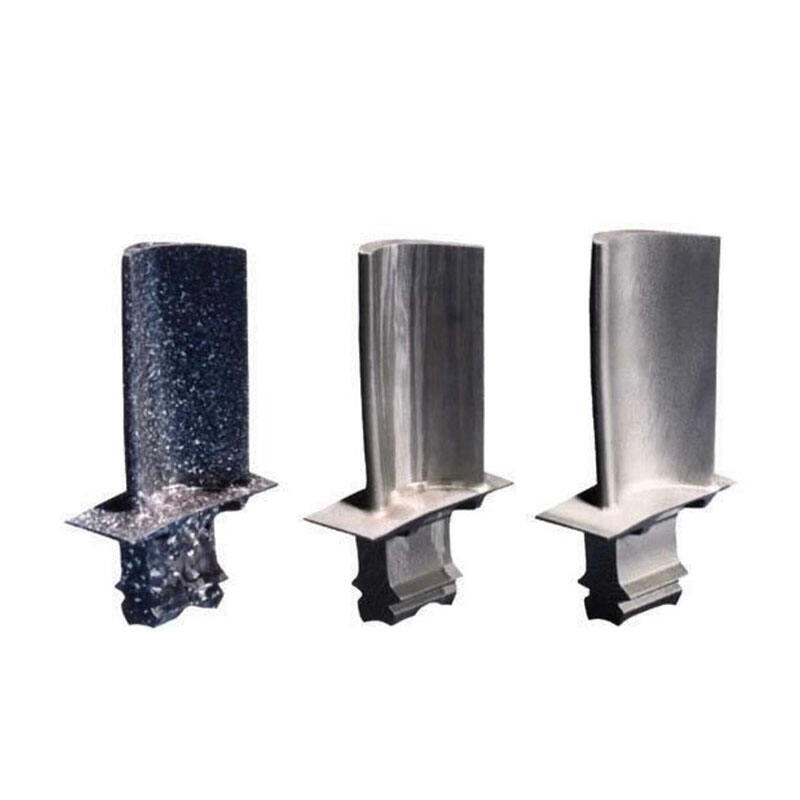
The turbine blade bears the centrifugal force andmomentum generated by the turbine blades,converts the kinetic energy of the airflow intomechanical energy, and provides power tosupport the operation of the turbine. Duringtheir high-speed rotation, they convert air flow energy into rotational kinetic energy on the shaft.

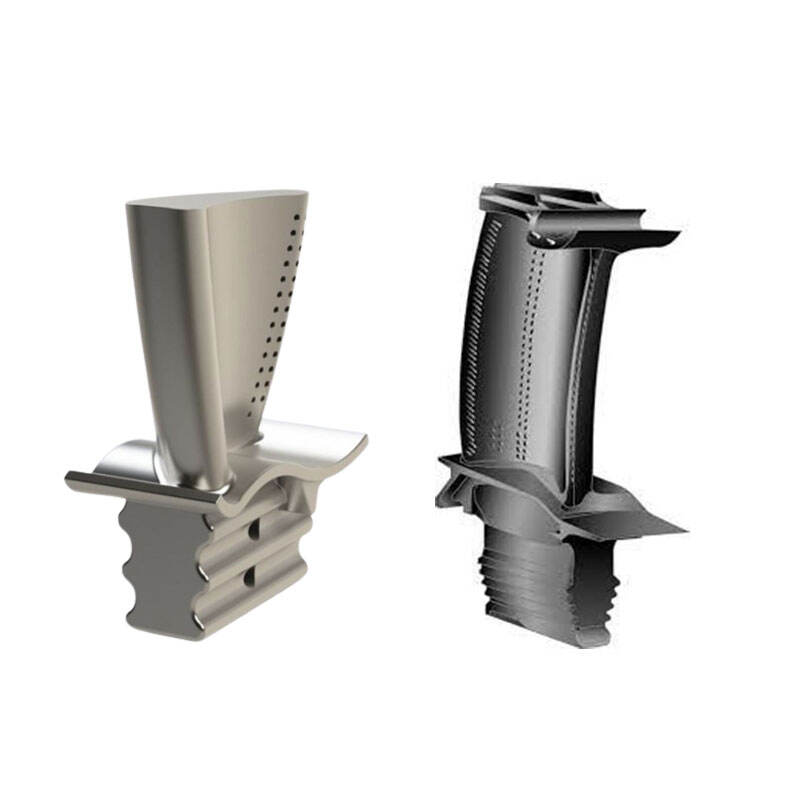
The design and manufacturing of theturbine disk need to ensure that it hassufficient strength and rigidity to withstand thecentrifugal force and inertial force caused byhigh-speed rotation. At the same time, theyneed to be balanced and aligned to ensurestable operation of the turbine.
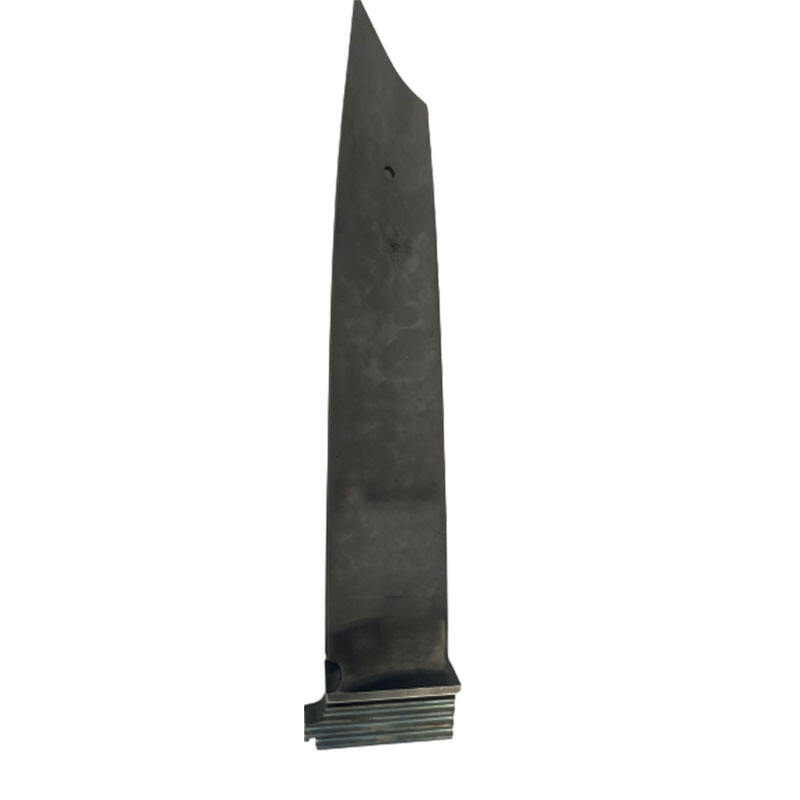

The turbine blade is the main support structurefor fixed blades. The blades are fixed on the diskto form a rotating blade array. These bladesgenerate power through the impact of airflow,thereby pushing the turbine disk to rotate anddriving related mechanical equipment tooperate.
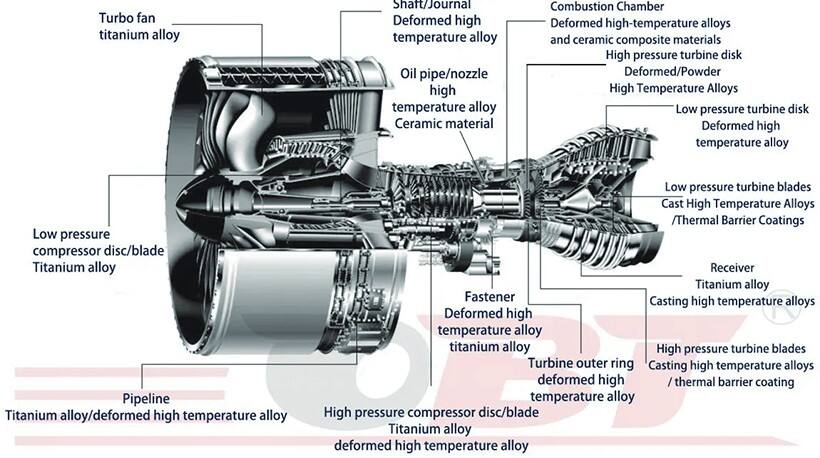
material
Inconel material Hastelloy material Stellite material Titanium material Nimonic Alloy material
In general, the turbine blade, as one of the core components of the turbine, assumes the important functions ofconnecting, supporting and transmitting power. Its design and manufacturing require precision workmanshipand high-quality materials to ensure efficient, stable and reliable operation of the turbine.
Turbine blade, as a key component of turbines, are widely used in many fields such as aerospace, energy, industry,transportation, and energy extraction, providing power support and energy conversion for various types ofmechanical equipment.
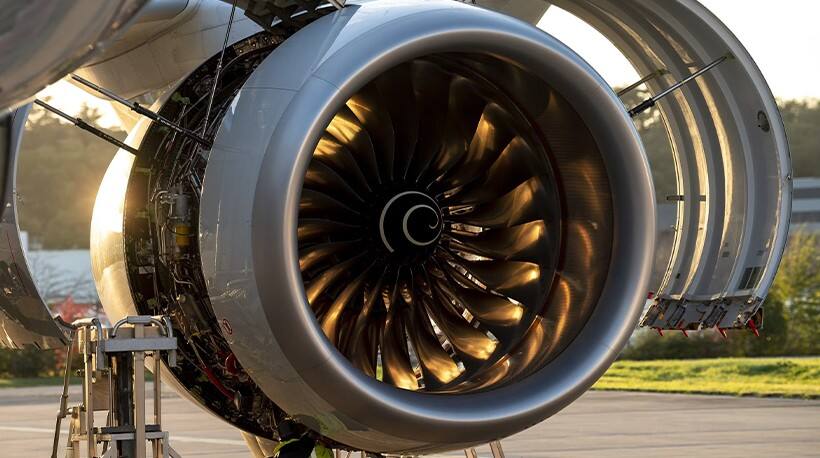

Aerospace field:Turbine discs are widely used in aerospace engines, including jet engines,turbofan engines, etc. They carry the turbine blades, which rotate to drive thecompressor, turbine and other related components to provide power tosupport the flight of the aircraft.

Energy industry:In the energy field, turbine disks are used in steam turbines, gas turbines,steam turbines and other equipment in various types of generating units.They convert gas or steam energy into electrical energy for use in powergeneration plants by turning the rotor of a generator.

Industrial field:In the industrial field, turbine disks are used in various types ofturbomachinery equipment, such as compressors, fans, pumps, etc. Theyrealize the compression, transportation or circulation of fluids or gasesthrough rotation and are used for power transmission and energy conversionin industrial production, manufacturing and processing processes.
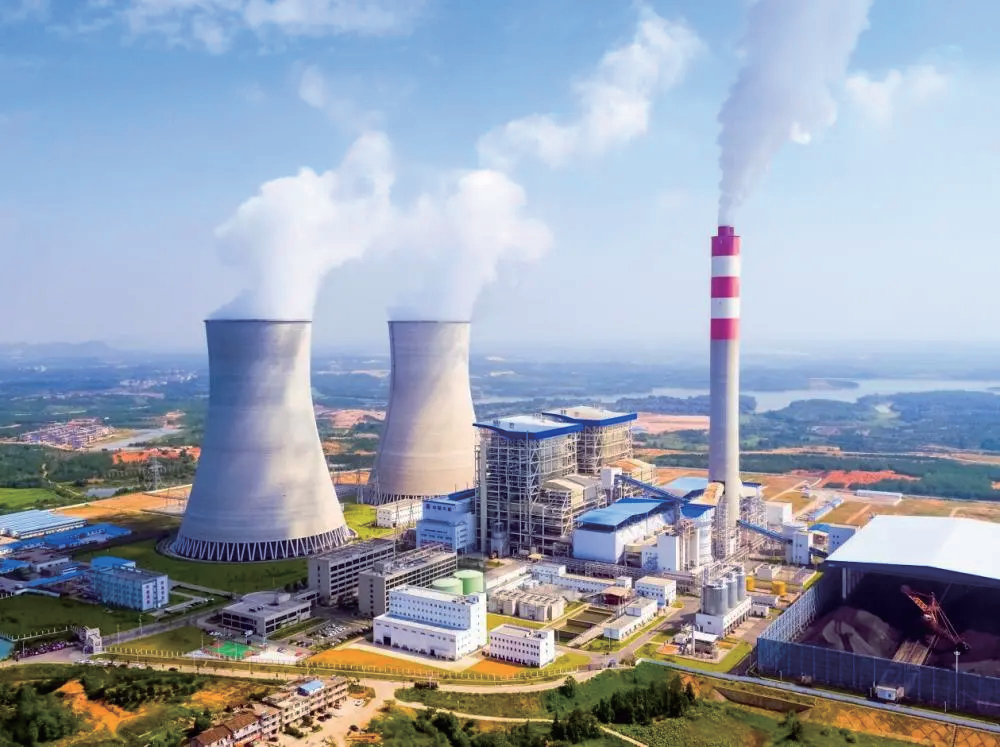

Industrial field:In the energy extraction field, turbine disks are used in various turbinemachinery equipment, such as oil and gas extraction equipment,hydroelectric power generation equipment, etc. They drive relatedequipment through rotation to improve energy extraction efficiency andproductivity
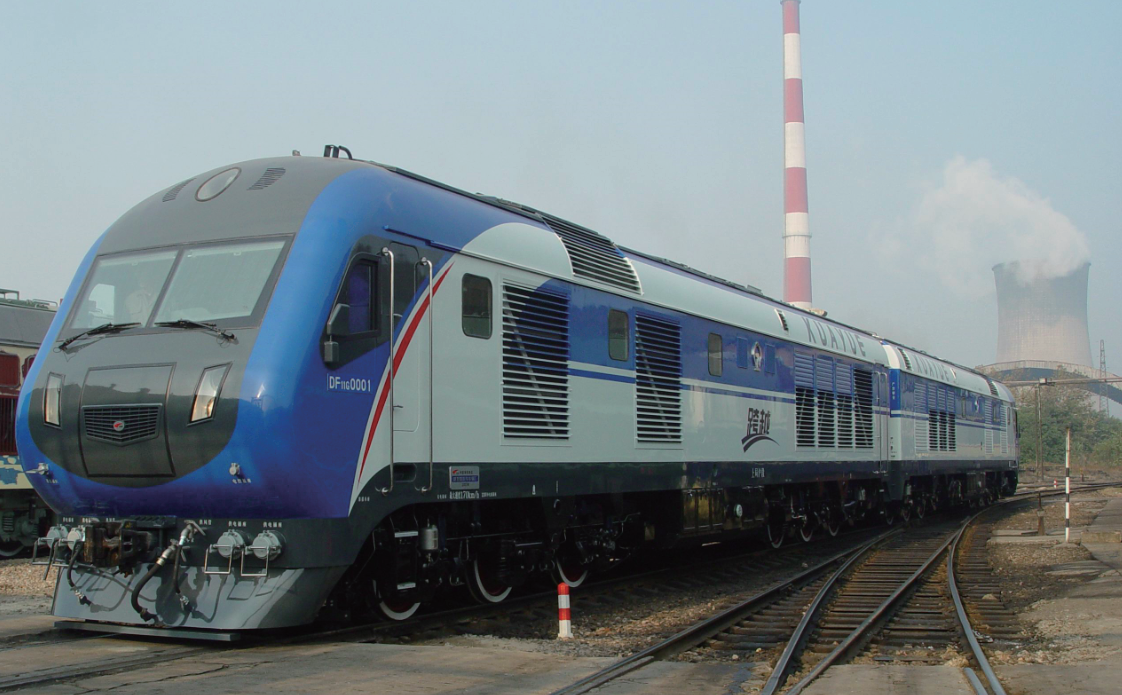

Transportation field:Turbine blades are used in turbochargers in automobile engines to improveengine power and fuel efficiency, as well as in turbochargers for transportationvehicles such as trains and ships.
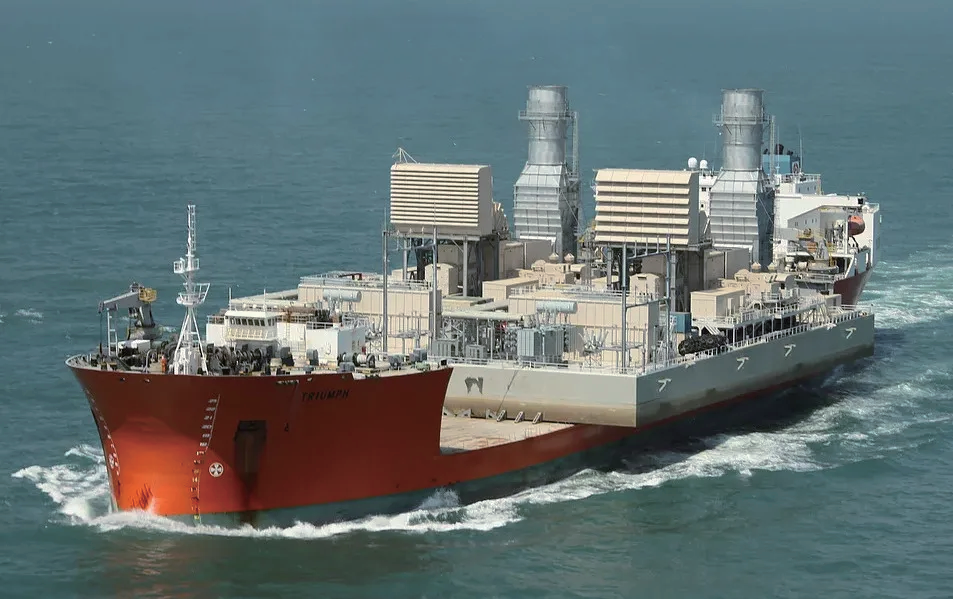

Shipbuilding industry:Turbine blades are used in ship power devices, such as turbochargersand marine turbines, to provide power to drive ships.
Our professional sales team are waiting for your consultation.