Turbine blades are divided into two categories: turbine guide blades and turbine working blades.
The main function of turbine guide vanes is to adjust the flow direction of the exhaust gas from the combustion chamber. The material operating temperature can reach up to over 1,100°C, and the stress borne by turbine guide vanes is generally less than 70MPa. This component is often scrapped due to distortion caused by large thermal stress, thermal fatigue cracks caused by sudden temperature changes, and burns caused by local excessive temperatures.

The turbine blades are located in the turbine engine with the highest temperature, the most complex stress and the worst environment. This component needs to withstand high temperatures and large centrifugal stress and thermal stress. The temperature it withstands is 50-100℃ lower than the corresponding turbine guide blades, but when rotating at high speed, due to the effects of aerodynamic force and centrifugal force, the stress on the blade body reaches 140MPa and the root reaches 280-560MPa. The continuous improvement of the structure and materials of turbine blades has become one of the key factors in improving the performance of aircraft engines.

The turbine blades, turbine shaft, turbine disk and other components together form the turbine of an aircraft engine. The turbine is the power source that drives the compressor and other accessories. The turbine can be divided into two components: the rotor and the stator:
Turbine rotor: It is a whole composed of turbine blades, wheels, shafts and other rotating parts mounted on the shaft. It is responsible for sucking high-temperature and high-pressure airflow into the burner to maintain the operation of the engine. The turbine rotor works at high temperature and high speed and transmits high power, so its working conditions are extremely harsh. When working at high temperature, the turbine rotor must withstand extremely high centrifugal force, and is also subject to the effect of aerodynamic torque, etc. The high temperature environment will reduce the ultimate strength of the turbine blade material, and will also cause creep and erosion of the turbine blade material.
Turbine stator: It is composed of turbine guide blades, outer ring and inner ring. It is fixed on the casing and its main function is to diffuse and rectify the airflow for the next stage turbine rotor to meet the speed triangle of the turbine working blades.
In order to improve performance indicators such as thrust-to-weight ratio, the requirements for the tolerance of aircraft engine and gas turbine blades to high temperature and high wind speed are constantly increasing. In mainstream aircraft turbofan engines, the turbine-driven compressor has a maximum of
The air entering the turbine engine rotates at a high speed of thousands of revolutions per second. The air is pressurized step by step in the compressor. The pressure ratio of the multi-stage compressor can reach more than 25. The pressurized air enters the engine combustion chamber, mixes with the fuel, and burns. The fuel flame needs to burn stably in the high-pressure airflow flowing at a high speed of more than 100m/s.
The high-temperature, high-pressure gas flow from the combustion chamber drives the turbine blades to rotate at a speed of thousands to tens of thousands of revolutions per minute. Usually, the temperature before the turbine exceeds the melting point of the turbine blade material. During operation, the turbine blades of modern engines usually have to withstand temperatures of 1600~1800℃, wind speeds of about 300m/s, and the huge air pressure caused by them.
Turbine blades need to work reliably for thousands to tens of thousands of hours in such an extremely harsh working environment. Turbine blades have complex profiles and use a large number of advanced manufacturing technologies such as directional solidification, powder metallurgy, complex hollow blade investment casting, complex ceramic core manufacturing, and micro-hole processing.
Turbine blades are one of the components of the "two machines" that have the most manufacturing processes, the longest cycle, and the lowest pass rate. The manufacture of complex hollow turbine blades has become the core technology in the current development of the "two machines".
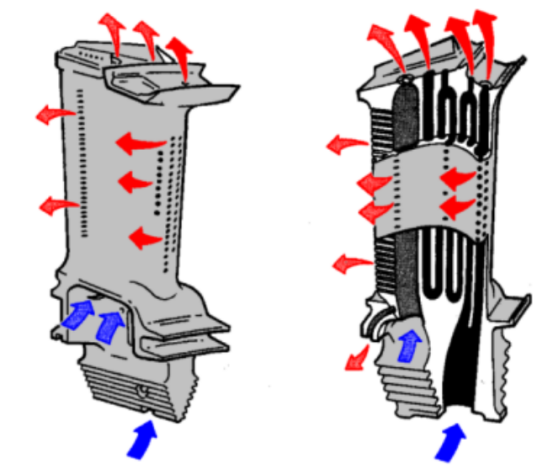
The blades in aircraft engines and gas turbines mainly include fan blades, turbine blades and compressor blades, of which the value of turbine blades accounts for about 60% of the total blade cost. Compared with fan blades, the raw materials of turbine blades are more valuable and more difficult to process.
As an important hot-end component of the engine, turbine blades require the use of high-temperature alloy materials. Their smelting technology requires high requirements, and some metal mineral resources are scarce. In terms of manufacturing process, turbine blades generally use investment casting to achieve thin walls and complex cooling structures. The manufacturing difficulty is significantly higher than that of other blades.
For example, the CFM56 aircraft engines widely used in the Boeing 737 series and Airbus 320 series have more than a thousand turbine blades, each costing more than 10,000 yuan. The unit price of turbine blades in certain parts even exceeds 100,000 yuan.
 Hot News
Hot News2024-12-31
2024-12-04
2024-12-03
2024-12-05
2024-11-27
2024-11-26
Our professional sales team are waiting for your consultation.